Fake IDs are a growing threat to your organization's security. They compromise borders, banks, and universities, causing huge losses and reputational damage. A layered security approach is your only effective defense.
The best way to prevent counterfeit ID cards is to adopt a multi-layered security strategy1. This means combining secure base materials, advanced printing techniques2 that are hard to copy, and a mix of both obvious (overt) and hidden (covert) security features3. This makes cards extremely difficult to replicate.

I've been in the security printing4 business for over 15 years, working directly with government agencies and large institutions. I've seen firsthand how sophisticated counterfeiters5 have become. But I've also seen which strategies work to stop them cold. It’s not about finding one magic bullet; it's about building a fortress with multiple walls. If a forger gets past one layer, they are stopped by the next. Let's break down how they attack and how you can build your defense, layer by layer.
How Do Counterfeiters Target ID Cards?
You think your IDs are secure? Counterfeiters are always finding new ways to exploit weaknesses. Their methods are often simpler and more effective than you might imagine, posing a real threat.
Counterfeiters attack ID cards by visually replicating them with common printers, altering data like photos or names, reusing stolen cards, or combining genuine and fake elements. A single security feature is not enough to stop these varied attacks.

To build a strong defense, you first need to understand the offense. In my experience, counterfeiters5 don't just use one method; they pick the easiest path. They look for the weakest link in your ID card's security. We generally see four main types of attacks.
Breaking Down the Threats
Understanding these methods is the first step to creating a card that can resist them. Each attack exploits a different vulnerability, which is why a single security feature is never enough.
| Attack Method | Tools Used | Primary Weakness Exploited |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Replication | High-resolution scanners, desktop printers, laminators | Lack of print features that fail when copied (e.g., microtext6, special inks7). |
| Data Alteration | Solvents, heat, sharp tools, replacement photos/text | Poor lamination8, no tamper-evident materials, simple fonts. |
| Card Reuse | Stolen or expired genuine cards | Lack of real-time verification systems9 or easily transferable data. |
| Hybrid Attacks | Combination of all the above | Reliance on just one or two security features3, lack of staff training. |
I remember a case with a corporate client. They had a decent hologram10 on their ID cards and thought they were safe. But counterfeiters5 were simply peeling off the top laminate layer, replacing the photo and name on the original card body, and then applying a cheap, generic laminate over it. The card body was genuine, but the data was fake. This is a classic hybrid attack. It taught us that every single layer, from the card material to the laminate, must be secure.
What is Material-Level Security for ID Cards?
Worried about basic fakes? The material of your ID card is your first line of defense. Using standard plastic is like leaving your front door unlocked for counterfeiters5 to walk right in.
Material-level security uses specialized card materials like multi-layered PVC or Polycarbonate11 with unique features like custom-colored cores. These materials are controlled, hard to source, and incompatible with consumer-grade equipment, stopping many fakes at the source.
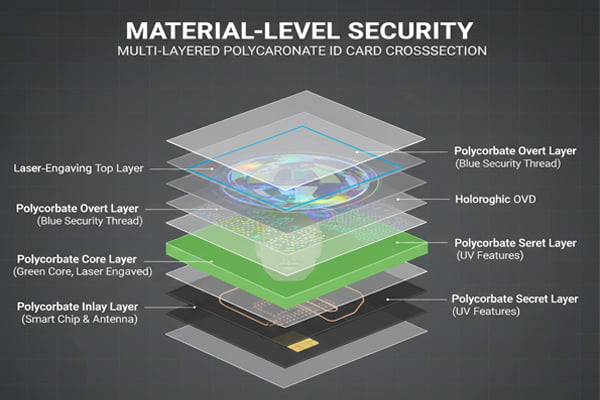
The foundation of a secure ID is the card itself. Before any ink is printed or any hologram10 is applied, the choice of material can defeat a huge percentage of counterfeiters5. Why? Because they rely on easily available materials. If they can't get the right card stock, the fake will look and feel wrong from the very beginning. This is where we start when designing a secure document for a government or university.
The Difference Between Standard and Secure Cardstock
Not all plastic is created equal. Most people think of an ID card as a single piece of plastic, but a secure card is a complex, layered structure. Polycarbonate11 (PC) is the gold standard for high-security documents like national ID cards and passports. Unlike PVC, which is made of separate layers glued together, a Polycarbonate11 card is fused together with heat and pressure into a solid, single block. This process, called lamination8, makes it impossible to separate the layers to alter data without completely destroying the card.
| Feature | Standard PVC Card | Secure Polycarbonate11 (PC) Card |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Layers are glued together. | Layers are fused into a solid block. |
| Tamper Evidence | Can be delaminated with heat/solvents to alter data. | Cannot be separated; attempts to alter it will visibly destroy the card. |
| Durability | Lasts 3-5 years. Prone to cracking. | Lasts 10+ years. Extremely durable and flexible. |
| Security Features | Limited to surface-level features. | Can embed features like laser engraving and security threads inside the card body. |
When we work with clients like the Bolivian government, specifying the card material is step one. We use a supply chain with strict controls, ensuring these security-grade materials12 don't leak out to the open market. By making the very foundation of the card a security feature, you create a huge barrier for counterfeiters5 before they even start.
How Does Print-Level Security Stop Fakes?
A high-quality scanner can copy almost any design. This makes your visible printed information vulnerable. But what if the features were designed to fail when they are copied by a machine?
Print-level security uses features like microtext6, guilloche patterns, and special inks7 (UV, OVI) that degrade, disappear, or change when scanned or photocopied. This makes accurate digital replication impossible and forgeries easy to spot.

Once you have a secure card base, the next layer is printing. But this isn't like printing a brochure. Security printing is a highly specialized field that uses techniques designed to defeat modern technology like high-resolution scanners13 and printers. The goal is to create elements that a human eye can see but a machine cannot properly reproduce. I've seen so many fakes that look good at first glance, but a quick check of the print quality reveals them instantly.
Why Scanners Can't Beat Security Printing
The trick is to use designs and inks that operate beyond the capabilities of standard equipment. For example, a commercial scanner and printer have a set resolution. We can print features that are too fine for them to capture.
-
Guilloche Patterns: These are complex, intricate line patterns made from a continuous line. When a scanner tries to copy them, it creates digital breaks and blurs in the line, resulting in a "jagged" or incomplete pattern on the fake. A genuine card will have perfectly smooth, unbroken lines when viewed under a magnifier.
-
Microtext: We print text so small (often 0.2mm or less) that it just looks like a thin line to the naked eye. To a scanner, it also just looks like a line. The scanner's resolution isn't high enough to capture the individual letters. On a fake, this line will be blurry or solid, while on a real card, a simple magnifying glass will reveal the hidden text, like "GENUINE DOCUMENT".
-
Specialty Inks: This is where it gets really interesting. We use inks that react to different conditions.
| Ink Type | How It Works | How It Defeats Counterfeiting |
|---|---|---|
| UV Ink | Invisible to the naked eye, but glows (fluoresces) under an ultraviolet (UV) light. | A forger won't know the hidden image or text is there. It provides a quick and easy verification check. |
| OVI Ink | Optically Variable Ink changes color when you tilt the card and view it from different angles. | This effect cannot be scanned or photocopied. A copy will only show one of the colors, not the color-shifting effect. |
| Infrared (IR) Ink | Some inks can absorb or reflect infrared light, making parts of a design appear or disappear under an IR camera. | This is a higher-level check for trained inspectors14 and is impossible to replicate with standard CMYK printers. |
These features work because they introduce effects that a simple copy-and-print process cannot handle. They force the counterfeiter to invest in industrial-level equipment, which is often impossible.
Why Use Both Overt and Covert Security Features?
Some security features3 are obvious, others are hidden. Are you using both? Relying only on visible features leaves you open to skilled forgers who can replicate what they can see.
Using both overt (visible) and covert (hidden) features creates a two-level verification system. Overt features like hologram10s allow for quick public checks, while covert features like UV text require special tools for expert verification, catching more sophisticated fakes.

The final layer of a great ID card strategy is about who checks the card and how they check it. You need features for everyone, from a security guard at a door to a forensic expert15 in a lab. This is the concept of overt and covert features. Overt means "out in the open," and covert means "hidden." A truly secure card needs a healthy mix of both. Relying on only one type is a common mistake that I see institutions make.
A Two-Tiered Verification System
Think of it as a security system for your house. You have the overt feature—a big, strong lock on the door that everyone can see. This deters casual burglars. But you also have the covert feature—a hidden motion sensor that silently alerts the police. This catches the more determined intruder who manages to pick the lock. ID card security works the same way.
| Feature Type | Purpose | Examples | Who Verifies It? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Overt (Level 1) | Quick, easy verification by the general public. Acts as a visible deterrent. | Custom Hologram, Color-Shifting Ink (OVI), Embossing, Lenticular Lens. | Anyone (e.g., security guards, bank tellers, police officers). |
| Covert (Level 2 & 3) | Deeper, more certain verification. Catches skilled forgers. | UV Fluorescent Ink, Microtext, Infrared Ink, Hidden patterns (scrambled indicia16). | Trained inspectors with special tools (e.g., UV light, magnifier, IR camera). |
One of the most powerful overt features is a custom hologram10. Many people buy cheap, "stock" hologram10s online that say "Secure" or "Genuine." Counterfeiters can buy the exact same hologram10s! A custom hologram10, designed and produced exclusively for your organization, is unique. We integrate your logo or specific symbols into the hologram10, making it a proprietary security feature. A counterfeiter cannot buy it; they would have to replicate it from scratch, which is an extremely expensive and difficult process. This single feature can elevate your security immensely.
By combining an easy-to-see custom hologram10 (overt) with hidden UV text (covert), you create a card that is both a strong visual deterrent and resistant to expert forgery.
Conclusion
In summary, protecting your ID cards requires a layered defense. Start with secure materials, add complex printing, and finish with a mix of overt and covert features.
Explore this resource to understand how a multi-layered approach can effectively prevent counterfeit ID cards. ↩
Learn about cutting-edge printing methods that enhance the security of ID cards and make counterfeiting difficult. ↩
Discover the most effective security features to include in ID cards to combat counterfeiting. ↩
Explore the specialized field of security printing and its role in preventing ID card fraud. ↩
Understand the tactics used by counterfeiters to exploit weaknesses in ID card security. ↩
Understand how microtext can be used as a security feature to prevent counterfeiting. ↩
Learn about the different types of special inks that enhance the security of printed documents. ↩
Learn about the lamination process and its importance in creating durable and secure ID cards. ↩
Explore how real-time verification can help prevent the reuse of stolen or expired ID cards. ↩
Discover how custom holograms can serve as a powerful deterrent against counterfeiters. ↩
Learn why Polycarbonate is considered the gold standard for high-security ID cards. ↩
Understand the importance of using security-grade materials to prevent counterfeit ID cards. ↩
Find out how counterfeiters exploit technology like high-resolution scanners to replicate ID cards. ↩
Explore the training required for inspectors to effectively verify the authenticity of ID cards. ↩
Understand the importance of forensic experts in verifying the authenticity of ID cards. ↩
Learn about scrambled indicia and how they can enhance the security of ID cards. ↩

