Worried your digital codes are easy to copy? Counterfeiters can clone QR codes, leaving your products and documents vulnerable. A physical layer is the key to true security1.
Physical security labels2 complement digital authentication by creating a trusted, tamper-evident foundation. Features like holograms and destructible materials3 ensure the digital code belongs to the genuine item. This prevents cloning and label swapping4, building a much stronger multi-layered defense.
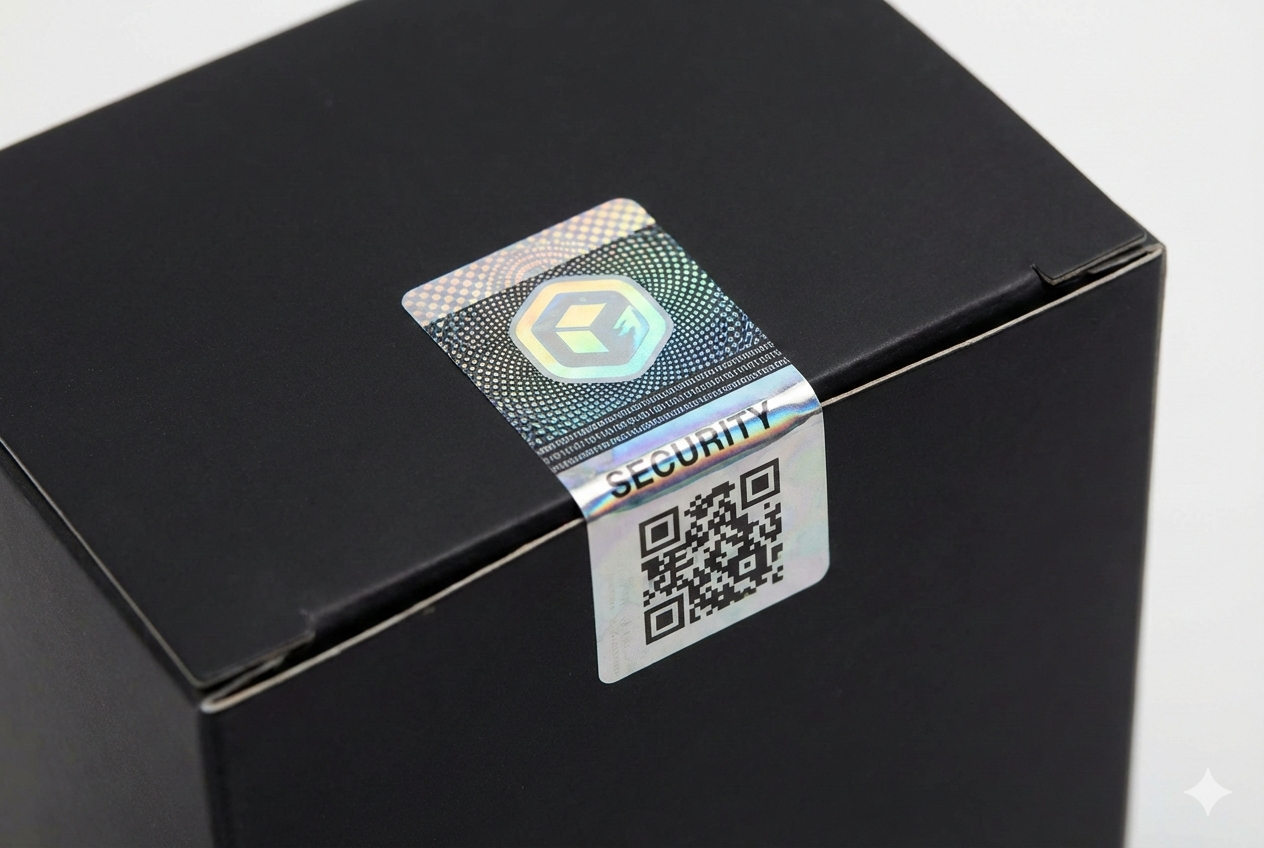

In my 15 years in the security printing industry, I've seen technology evolve rapidly. We've moved from simple watermarks to complex digital systems. But one thing has never changed: the smartest security is layered security5. Relying on just one method, especially a digital one, leaves a door open for counterfeiters. The real strength comes from making the physical and digital worlds work together. Let's explore why this hybrid approach is no longer just an option, but a necessity.
Why Is Digital Authentication Alone Not Enough to Stop Counterfeits?
Are you relying only on a QR code or NFC chip? This creates a false sense of security. Counterfeiters can easily copy these digital triggers and place them on fake items.
Digital authentication alone is not enough because it only verifies data, not the physical object itself. This means QR codes can be cloned6, databases can be tricked, and authentic labels can be swapped onto fake products. Without a physical anchor, digital systems are vulnerable.

I once worked with a client who had a brilliant app for verifying their products. A simple scan of the QR code on the package would confirm its authenticity in their database. The problem was, counterfeiters just copied that same QR code and printed it on thousands of fakes. The app would say the product was real because the code was real, but the product in hand was a cheap imitation. This highlights the core weakness of a digital-only approach. It creates a gap between the data and the physical item.
The Cloning Risk
The most common issue is cloning. A QR code or NFC tag is just data. A counterfeiter can easily read this data and replicate it endlessly. They can create a perfect digital copy and apply it to a fake product. Your system sees a valid code, so it approves the item, even though the item itself is not genuine.
The Physical Gap
Digital systems check information, not materials. Your database can confirm that serial number XYZ is valid. But it cannot tell you if that serial number is printed on genuine security paper or on a cheap photocopy. This is the physical gap. The system authenticates the "idea" of the product, but not the actual product in the user's hand.
The Label Swapping Problem
What if the label itself is authentic? Counterfeiters can buy one genuine product, carefully remove its security label with the valid QR code, and place it on a counterfeit item. This is called label swapping4. The code is legitimate and tied to a real product, but it's now attached to a fake. Unless the label is designed to be destroyed upon removal, this is a major security risk.
| Vulnerability | Digital-Only System | Hybrid (Physical + Digital) System |
|---|---|---|
| Code Cloning | High risk. Codes can be easily copied. | Low risk. Tamper-evident label protects the code. |
| Label Swapping | High risk. Labels can be moved to fakes. | Very low risk. Destructible labels prevent reuse. |
| Material Check | Not possible. Cannot verify the physical item. | Possible. Overt features allow instant visual checks. |
What Makes a Physical Security Label Truly Secure?
Think all labels are the same? A standard sticker offers zero protection. A true security label is engineered with complex features that are incredibly difficult for criminals to replicate.
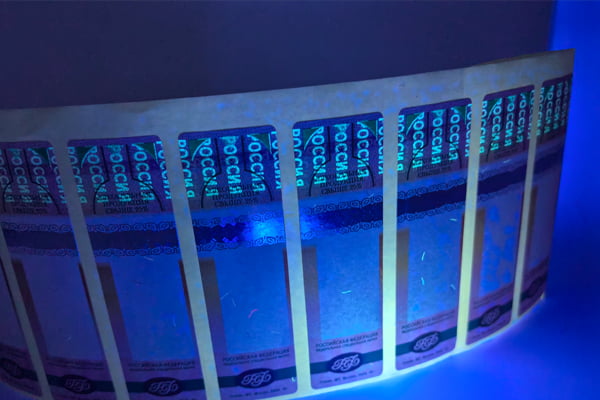
A truly secure physical label integrates multiple hard-to-copy features. These include custom holograms7, tamper-evident materials that self-destruct, and covert elements like UV ink or microtext8. These layers make the label itself a powerful anti-counterfeiting tool.
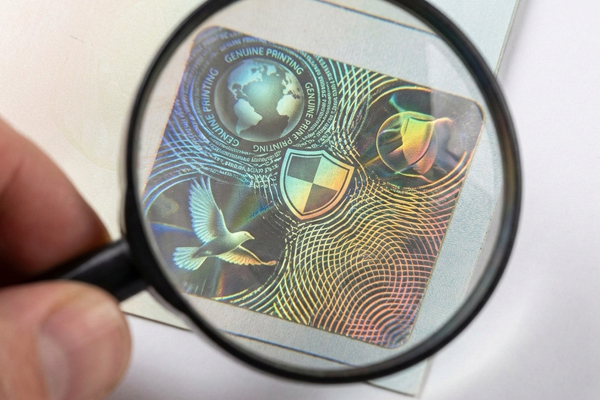

We create these features every day for governments and major corporations. It's not about just one trick; it's about combining multiple technologies into a single label. A counterfeiter might be able to mimic one feature, but replicating three or four different advanced technologies accurately is nearly impossible. This complexity is what provides real security. It raises the bar so high that it becomes too expensive and difficult for counterfeiters to even try.
Overt and Covert Features
A good security strategy uses a mix of visible (overt) and hidden (covert) features.
- Overt Features: These are things anyone can see and check without special tools. A custom hologram or a color-shifting ink patch are great examples. They act as a first-line-of-defense and a visible deterrent.
- Covert Features: These require a special tool or knowledge to verify. UV-fluorescent ink that only appears under a blacklight, or microtext that can only be read with a magnifying glass, are common examples. These are for trained inspectors or officials to use for definitive verification.
Tamper-Evident Design
The ability to prove a label has been tampered with is critical. This is where tamper-evident materials come in.
- VOID Patterns9: When someone tries to peel this type of label off, it leaves behind a pattern of words, like "VOID" or "OPENED," on both the surface and the back of the label. The label cannot be reapplied.
- Destructible Materials10: These labels are made from a very brittle material, like eggshell vinyl. If anyone tries to remove it, the label shatters into tiny pieces, making it impossible to remove in one piece and reuse.
Unique Identifiers
Every secure item should be unique. We use variable data printing11 to put a unique serial number, QR code, or barcode on every single label. This ensures that each item can be individually tracked and authenticated, preventing counterfeiters from using one valid number for a batch of fakes.
How Do Physical and Digital Security Actually Work Together?
Wondering how these two very different technologies connect? The physical label acts as a secure gateway to the digital world, ensuring the information you access is linked to a genuine item.
Physical security labels2 create a trusted entry point for digital authentication12. A user first visually inspects the physical features, like a hologram. This confirms the label is likely genuine before they scan the QR code. The physical security prevents the digital code from being moved or copied.

Think of it like a bank's security. The big metal vault door is the physical security. Your PIN is the digital security. You need both to access your money. You can't just walk up to any wall and enter your PIN; you have to go to the specific, secure ATM. The physical security label works the same way. It tells you, "This is the right place to scan. This is a genuine item." This simple, two-step process creates a powerful defense.
The Trusted Bridge
Before a customer, inspector, or official scans a QR code, their first instinct is to look at the product. If they see a complex, high-quality holographic label, it immediately builds trust. They feel confident that the product is real. This physical verification is the first and most important step. The physical label acts as a trusted bridge. It connects the physical product in their hands to the digital information on their screen. Without that bridge, the digital data has no real-world context.
A Multi-Layered Defense
Combining physical and digital methods creates a multi-layered security system13s://genuine-printing.com/choosing-the-best-security-paper/)5 system. Each layer protects the others.
| Security Layer | Purpose | How it Works |
|---|---|---|
| Layer 1: Overt Physical | Instant Visual Check | User sees the hologram or color-shifting ink. This deters casual counterfeiters. |
| Layer 2: Digital | Data Verification | User scans the unique QR code to check the database for product info, origin, etc. |
| Layer 3: Covert Physical | Expert Verification | An official uses a UV light or magnifier to check for hidden features, confirming authenticity. |
| Layer 4: Tamper-Evidence | Integrity Check | If the label is damaged or shows a "VOID" pattern, it's clear it has been tampered with. |
This layered approach means that even if a counterfeiter somehow gets past one layer, the other layers are still there to stop them. For example, even if they could replicate a hologram perfectly (which is very difficult), the unique QR code would still be linked to a single item in the database. And the tamper-evident feature would prevent them from moving a real label to a fake product.
Where Are These Hybrid Security Solutions Most Effective?
Is this kind of high-level security only for governments? Not at all. Any industry dealing with high-value goods, sensitive information, or public safety can benefit from this powerful combination.
Hybrid security solutions are most effective in sectors where authenticity is critical. This includes government documents like ID cards and tax stamps, brand protection for luxury goods, and regulated products like pharmaceuticals, where counterfeits pose a direct threat to public health and safety.

We have provided security solutions for everything from university diplomas to tax stamps for the Bolivian government. The core challenge is always the same: how do you ensure the item in someone's hand is 100% authentic? The stakes are different for each industry, but the solution often involves this blend of physical and digital security.
Government Documents and Certificates14
This is one of the most critical areas. Passports, ID cards, visas, and tax stamps must be protected against fraud. We embed security threads, watermarks, and holographic overlays into the paper or card itself. Then, we add a smart chip or a unique QR code that links to a government database. This makes it possible for a border agent to quickly verify a document's physical features and then confirm the holder's identity digitally. For certificates and diplomas, this prevents people from faking qualifications.
Brand Protection and Supply Chains15
Luxury brands lose billions to counterfeiters. We help them by creating secure labels that combine a custom hologram with a serialized QR code. Customers can scan the code to verify the product's authenticity and register their purchase. This does two things: it reassures the customer and it provides the brand with valuable data about their supply chain. It helps them see where fakes are appearing and shut them down.
Pharmaceuticals and Regulated Goods16
In the pharmaceutical industry, a counterfeit product can be deadly. Here, security is not just about money; it's about public health. We use tamper-evident seals with unique identifiers on medicine packaging. A pharmacist or patient can check that the seal is intact and then scan a code to verify the drug's batch number and expiration date in a secure database. This ensures that the medicine is safe and has not been tampered with.
Conclusion
Combining physical security labels with digital authentication is the strongest way to protect your products and documents. It creates a complete, multi-layered defense that is extremely difficult for counterfeiters to beat.
Learn why incorporating a physical layer is essential for enhancing the security of your digital codes and preventing counterfeiting. ↩
Discover how physical security labels can provide a tamper-evident foundation to protect your products from counterfeiting. ↩
Explore how these features can prevent cloning and label swapping, strengthening your product's defense against counterfeiting. ↩
Discover how label swapping can undermine your security efforts and what measures can prevent it. ↩
Find out how combining multiple security methods can create a robust defense against counterfeiters. ↩
Understand the risks associated with QR code cloning and how it can compromise your product's authenticity. ↩
Explore how custom holograms can act as a visible deterrent to counterfeiters and enhance product security. ↩
Understand how these hidden features can provide an additional layer of security for your products. ↩
Learn how VOID patterns can indicate tampering and prevent the reuse of security labels. ↩
Find out how destructible materials can ensure that labels cannot be removed and reused on counterfeit products. ↩
Discover how variable data printing can provide unique identifiers for each product, preventing counterfeiting. ↩
Learn how physical labels can ensure that digital authentication is linked to a genuine item. ↩
Explore how combining physical and digital security methods creates a comprehensive defense against counterfeiting. ↩
Learn about the security measures used to protect important government documents and certificates from fraud. ↩
Discover how combining physical and digital security can safeguard brands and improve supply chain integrity. ↩
Understand the importance of security in the pharmaceutical industry and how it protects public health. ↩